Knowledge Repository
Explore our collection of knowledge resources and documents.
Find valuable information below.
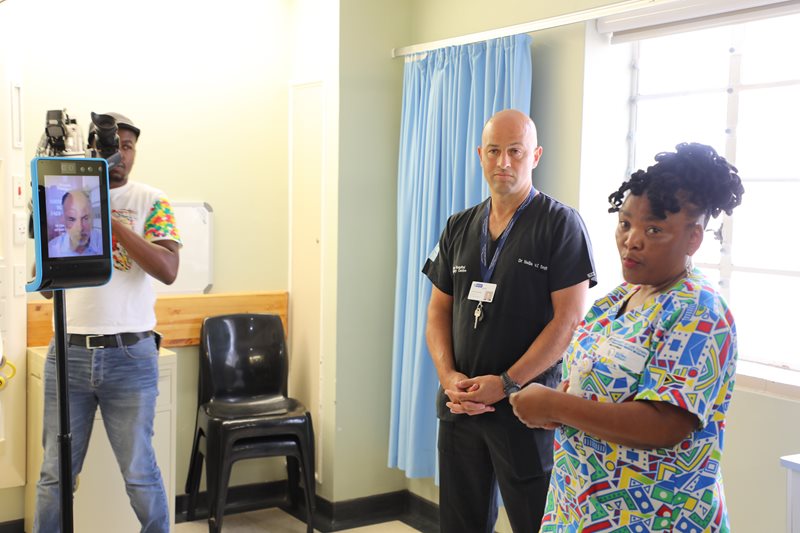

TeleICU – Saving Lives from a Distance
George Regional Hospital (GRH) and Groote Schuur Hospital (GSH) collaborated to implement and telehealth service using robotics, enhancing critical care access for Eden and Central Karoo districts. This initiative has bridged geographical barriers, providing timely specialist consultations form GSH to GRH’s ICU. This approach aims to sustainably enhance healthcare delivery across the region through increased access to expertise as well as enhanced knowledge and skills transfer.
Date: 2026/01/29
Version: 0.1
Tags:
Public Health Innovations
Telehealth
eHealth

Saving Blood, Saving Lives
Blood products are a life saving resource and are essential to a successful healthcare system. The challenge is that they are both a scarce and expensive. Edendale Hospital was deemed one of the worst provincial performers in terms of the amount and cost of blood products used, misuse and ordering of products, this despite having a blood bank on site. Their challenge was to figure out an innovative strategy to ensure the correct use of blood products, decrease the amount of blood products used and also reduce expenditure. The result was a simple, yet effective strategy that sought to avoid inappropriate use of blood products.
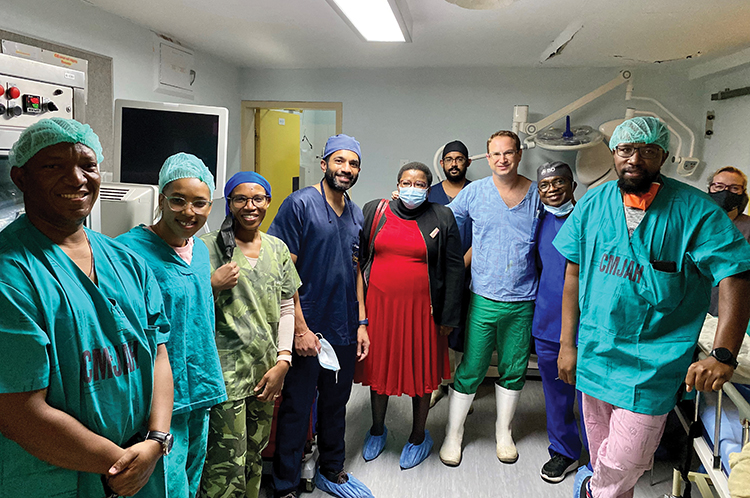

Early Prostate Cancer Treatment Project
Radiation Oncology at Charlotte Maxeke Johannesburg Academic Hospital (CMJAH) and Urology at CMJAH and Chris Hani Baragwanath Academic Hospital (CHBAH) have long waiting lists for patients to receive prostate cancer treatment. Treatment options involved 7-weeks of daily external beam radiotherapy (EBRT) or operations (radical prostatectomy) with extended hospital recovery stays. With limited linear accelerator time and surgical theatre time, patients wait up to 5 years before treatment, and some upstage their cancer. Using prostate brachytherapy, radioactive seeds are inserted into the prostate to treat the prostate cancer. The procedure takes 1 hour (vs. 4-5 hours for a radical prostatectomy), and patients are discharged the next day. Success rate is equivalent to the other treatment modalities for early-stage prostate cancer, and cures over 90% of patients.
.png)
Telehealth Implementation within the Paediatric Speech Therapy Outpatient Service
The implementation of telehealth into the paediatric speech therapy outpatient service was initiated as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic. Due to the pandemic, especially during level 5 and 4 lock down, patients were not able to access outpatient services. As restrictions were eased, it was evident that attending multiple appointments further added to the financial burden being faced by families as well as increasing their risk of exposure to COVID 19. As a result of these factors the innovation within the paediatric speech outpatient service through telehealth ensured that all patients still had access and were receiving speech therapy services, in accordance with patients’ right to therapy. Patients were provided with speech, language and feeding intervention in the comfort of their homes. This ensured that all patients are receiving the intervention that they have the right to receive, which is crucial, especially with Early Childhood (ECI) Intervention, which is a priority throughout all paediatric speech services. The reason being that ECI provides the opportunities for future success if intervention strategies are implemented from a young age. Essentially, it improves their overall outcomes.
Date: 2026/01/28
Version: 0.1
Tags:
Public Health Innovations
Disability Interventions/Prevention
Telehealth

Multi-Disciplinary Package of Care for Lower Limb Replacement Arthroplasty Patients
In South Africa, there is an ongoing major challenge of extensive waiting lists of arthroplasty patients. To manage this challenge would require huge sums of money. Following the onset of COVID-19 pandemic, this challenge became worse particularly with the subsequent cancellation of elective surgeries. At Chris Hani Baragwanath Hospital (CHBAH), it would take as long as two years for patients to receive an arthroplasty operations as per the waiting list registry kept at the unit, not only did this attract bad media publicity, it also inevitably became a major political concern. In response, the orthopaedic physiotherapists at CHBAH developed a solution in the form of a multi-disciplinary package of care.
Date: 2026/01/28
Version: 0.1
Tags:
Public Health Innovations
Disability Interventions/Prevention
Multidisciplinary Approach to Healthcare
Telehealth
Expansion of Clubfoot Services and Training Project
Clubfoot is a common congenital musculoskeletal disorder that causes mobility impairment. It is one of the leading causes of physical disability in children, particularly in low to middle income countries. This is true, despite the fact that it is a treatable condition. Clubfoot is a deformity in which an infant's foot is turned inward, often so severely that the bottom of the foot faces sideways or even upward. The condition most often presents at birth and is caused by a shortened Achilles tendon. Generally, there is a lack of trained mid-level personnel to provide clubfoot treatment in Africa. In addition, there is no standard training courses. In Gauteng province, Clubfoot is generally managed in Academic Hospital clinics which are run by Orthopaedic Surgery Departments. This placed a huge burden on these facilities which are few while also forcing patients and their families to travel longer distances to seek treatment elsewhere. The Charlotte Maxeke Johannesburg Academic Hospital came up with a solution to deal with this challenge.
Date: 2026/01/27
Version: 0.1
Tags:
Public Health Innovations
Disability Interventions/Prevention
Multidisciplinary Approach to Healthcare

Infrastructure Reporting Model (IRM)
The National Treasury’s Infrastructure Reporting Model (IRM) is a reporting system for infrastructure projects implemented across government. The design objectives of the system link each project to an approved/allocated budget and measures performance (financial and non-financial) until the project is complete. The distinct feature between the IRM and a project management system is that the IRM is linked to the RSA budget cycle in terms of allocation of funds to projects, project selection as well as reporting and advocates for spending within allocated or approved budgets to avoid over-commitments when funds are not available.
Date: 2026/01/27
Version: 0.1
Tags:
Infrastructure Development
Project Management Automation

Early Childhood Intervention in Neonatal and Maternal Health
The project was started following an Early Childhood Intervention (ECI) training in February 2020, where three Charlotte Maxeke Johannesburg Academic Hospital (CMJAH) Therapeutic Service employees (Occupational Therapist, Speech Therapist and Physiotherapist) identified a need to initiate a Task Team to address the specific early intervention needs of the Paediatric community at CMJAH. While there is an existing multidisciplinary team focus within the CMJAH Paediatric Therapeutic service unit, the high burden of care and fast-paced work environment has resulted in challenges in collaboration in planning, organising, evaluating, and implementing new strategies within the ECI service delivery. Therefore, the key reason for initiating the task team is to provide a framework for the early intervention services and a guidance to plan, monitor and evaluate these services towards holistic patient care. The primary focus of the CMJAH ECI Task team for the past 12 months pertains to evaluations and innovations within the neonatal and maternal health target populations. This innovation plays a pertinent role in ensuring that systems are implemented for early detection and identification, assessment, and management of patients with high-risk birth factors. This is important to reduce the impact of the vulnerabilities associated with high-risk birth factors on a child’s holistic development within their family context.
Date: 2026/01/23
Version: 0.1
Tags:
Public Health Innovations
Multidisciplinary Approach to Healthcare
Neonatal Health
Maternal Health

The Early Hearing Detection and Intervention (EHDI) Programme
Congenital hearing loss occurs most frequently at birth. The World Health Organization (2010) indicated newborn hearing impairment averages around 6 per 1000 births. Children develop language, communication, and cognitive skills by hearing. The early identification of hearing loss is necessary for healthy child development. With advancements in the method of assessing hearing status of newborns objectively, the implementation of a universal newborn hearing screening (UNHS) programme is an effective system to identify hearing loss early (Das et al., 2020). While early hearing detection and intervention (EHDI) focuses on the overall journey of the child from identification, diagnosis, and management (Moodley & Storbeck, 2015). The South African government recognises the value of UNHS; however, it has not been adopted within the public health sector that services approximately 80% of the population (Kanji, 2018). Recent studies have widely indicated that the implementation of an EHDI programme will have adverse economic effects in future.
Date: 2026/01/23
Version: 0.1
Tags:
Public Health Innovations
Disability Interventions/Prevention
.jpg)
Centre for Children with Special Needs
Bertha Gxowa Hospital started the Centre for Children with Special Needs to deal with challenges that faced children with special needs, their mothers and care givers who were spending more than a day when visiting the hospital for services. Children with special needs were seen on one-on-one basis in the past which resulted in delays. Appointments were booked on the same day by different parents and caregivers. This became overwhelming with the high referral rate. Waiting periods grew longer and patients were seen less frequently. As a result, the Cerebral Palsy Clinic also known as the Centre for Children with Special Needs was established. Tags:
Date: 2026/01/23
Version: 0.1
Tags:
Public Health Solutions
Disability Intervention
Waiting Times Reduction
Multidisciplinary Approach to Healthcare

MomConnect
South Africa needs significant improvements to meet the Millenium Development Goals (MDGs) for child and maternal mortality. It is recognised that a large number of child and maternal deaths could be avoided if some basic interventions are implemented at scale. Many pilot projects in a number of countries, have successfully used cell phone technology as a tool to improve interventions which have been shown to improve Maternal and Child Health (MCH) outcomes. In South Arica, virtually every pregnant woman has access to cell phone. It is therefore considered that appropriate access to cellphone technology has the potential to accelerate interventions of proven value.
Date: 2026/01/22
Version: 0.1
Tags:
mHealth
Mobile Technology Solutions
Public Health Innovations
Maternal Health
Neonatal Health
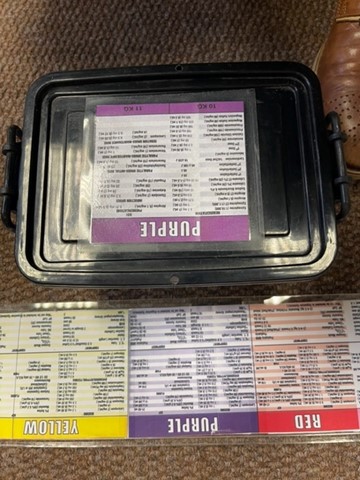
Broselow Emergency Reference Tape Inspired Resuscitation Boxes
Pediatric resuscitation can be very daunting at a Primary Healthcare (PHC) facility. This can be particularly stressful with new staff in the emergency with the rotation of staff at a PHC facility. Every PHC Emergency Center has a pediatric resuscitation trolley that is generally well stocked. Due to infrequent pediatric resuscitations at primary healthcare facilities and the rotation of clinical staff resuscitations are a challenge. There is often a rush to look for the appropriate size equipment and furious search for appropriate protocols on smart phone applications to find the correct dosages. The Mitchells Plain Community Health Center came up with a solution to this challenge.
Date: 2026/01/22
Version: 0.1
Tags:
Pediatric Health
Public Health Innovations
Quality Improvement Project on Triaging and Fast-tracking Maternity Patients
Patients at the Themba Hospital in Mpumalanga province were not triaged. They were attended on the basis of who came first unless labour was imminent or there was an emergency. This resulted in cases such as fetal distress, cord prolapse or uterine rupture not diagnosed immediately because patients had to wait for their turn. Many cases were not monitored. This contributed to poor maternal and fetal outcomes. The project aimed at creating a standardised and easy to use system for assessing and prioritising urgency of patients who were presented to the labour ward.
Date: 2026/01/22
Version: 0.1
Tags:
Maternal Health
Public Health Innovations
Neonatal Health

Hospital and Emergency Centre Tracking Information System (HECTIS)
It is universally accepted that the Emergency Centre (EC) is the coal face of the healthcare service delivery platform at all levels of care from primary to specialised institutions. As a consequence, the management and efficiency of this service will directly impact on the quality of patient outcomes. The Western Cape Department of Health historically utilised large amounts of paper-based registers to track the number and movement of patients through the Emergency Centre. This led to large amounts of redundant capturing of patient data at multiple touchpoints, poor access and quality of any patient EC Data, and an inability to manage the chaos which prevails at most Emergency Centres. The ECs are a high service pressured area and any relief to staff would have a major impact as well as enable better clinical and operational management of services. In response to this challenge, the HECTIS (Hospital and Emergency Centre Tracking Information System) application was developed. It was initially piloted at 4 Emergency Centres and iteratively improved over time. During COVID-19 it showed massive utility and is now, over the last 18 months, being scaled up to every public sector Emergency Centre in the province.
Date: 2026/01/22
Version: 0.1
Tags:
Patient Management System
Public Health Innovations
Government In-house Solutions
CDM Talk App
The Capricorn District Municipality (CDM) developed the CDM Talk App as part of its digital transformation to bring government closer to the people. It is a citizen-centric mobile and web platform designed to improve communication, customer care, service delivery tracking, and transparency between the municipality and its communities.
Date: 2026/01/20
Version: 0.1
Tags:
Local Government Innovation
Municipal App
Government In-house Solution
City Solve
Midvaal Local Municipality initiated the City Solve project to address growing challenges in managing land use applications and building plan approvals. With rapid urbanisation and increasing development pressures, the manual processes in place were inefficient, leading to delays, errors, and citizen dissatisfaction. The municipality recognised the need for a more streamlined, transparent and efficient system.
Date: 2026/01/20
Version: 0.1
Tags:
Local Government Innovation
Municipal App
Government In-house Solution
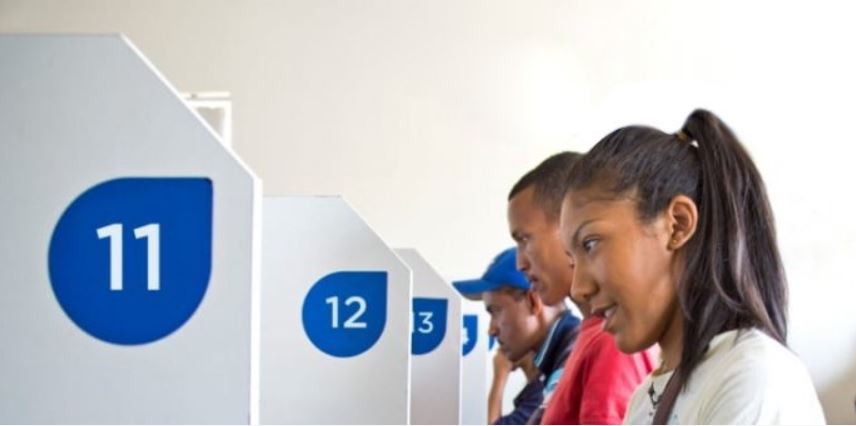

Repurposing Service Delivery Points (eKiosks)
The Repurposing Service Delivery Points later renamed eKiosks Project is a strategic initiative by the Western Cape Government to enhance digital service delivery in rural areas. It leverages existing infrastructure at ecentres, libraries, museums, and other service points to provide citizens with direct access to government services via self-service digital kiosks. The project follows a two phase approach: Phase 1 involved feasibility assessments at service site, while Phase 2 piloted eKiosks at two rural museums and ten libraries, in partnership with the Department of Cultural Affairs and Sport. Key components include infrastructure upgrades, frontline staff training, and a robust change management plan to ensure stakeholder buy-in. The initiative is a response to community feedback from the 2022 Listening Campaign, which highlighted barriers to accessing government services.
Date: 2026/01/06
Version: 0.1
Tags:
Integrated Government Solutions
Citizen Access to Digital Services
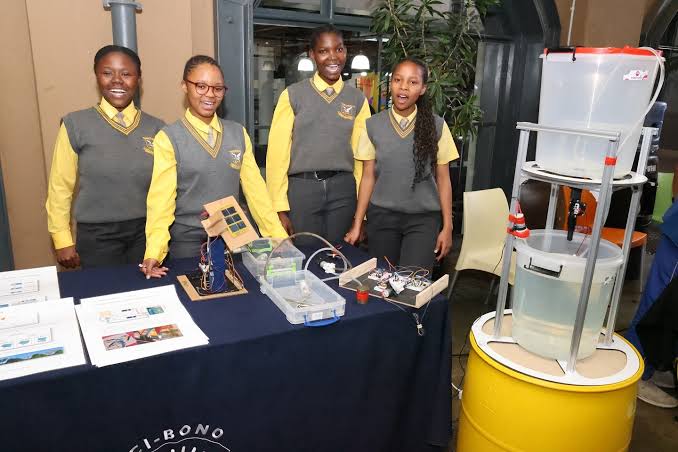

Gauteng Multi-Certification Skills Programme
The Gauteng Department of Education's Multi-Certification Skills Programme is designed to blend academic learning with practical and future focused skills. This learner-centred approach aims to produce well-rounded individuals, equipped to thrive in the 21st century. By integrating diverse skill sets into the curriculum, the programme promotes adaptability, innovation and inclusivity. Starting from Grade R, learners receive swimming lessons to establish water safety and fitness. From Grade 4 they get first aid training and begin coding and robotics education, which continues through to Grade 12. Entrepreneurship is introduced in Grade 5, while Grade 7 learners start learning sign language. Music enhancement in Grade 8 and 9 encourages creativity and Microsoft Digital Skills training from Grade 8equips learners for modern workplace. In Grade 9, learners are exposed to advanced technologies such as drone technology and Rocketry, sparking interest in STEM careers. Artificial Intelligence in introduced in Grade 12, preparing students for technology-driven futures. Overall, the Multi-Certification Programme is building a generation of competent, socially responsible and technologically adept learners.

Project Readiness Matrix Automation
The Department of Infrastructure Development (DID) implemented a Project Readiness Matrix (PRM) to enhance project governance and execution. The PRM is a structured evaluation technic used to gauge project readiness across gates, stages and milestones before moving to the next phase. It lowers the possibility of delays and cost overruns by ensuring that resources, documentation, and compliance requirements are taken care of up front. The PRM improves accountability, efficiency, and transparency in the province's infrastructure portfolio management by providing a standardised framework.
Date: 2026/01/06
Version: 0.1
Tags:
Infrastructure Development
Project Management Automation
Meter Reading Platform
The Meter Reading Collection System is a web-based solution designed to digitise and optimise the collection, validation and processing of household utility meter readings (water and electricity). The system replaces manual processes that were time consuming with an unacceptable amount of billing errors. This system enhances efficiency, accuracy and transparency in utility management.
eRecruitment Management System: Matjhabeng Local Municipality
Matjhabeng Local Municipality internally developed an eRecruitment Management System (eRMS) by the ICT department in collaboration with the HR department. The HR department had challenges with processing large volumes of job applications, which resulted in delays in the appointment of critical staff members. The recruitment process took longer and was full of mistakes. The system sought to improve efficiencies in the recruitment process.
Date: 2025/12/09
Version: 0.1
Tags:
Local Government Innovations
Government In-house Solutions
Human Resource Solutions

Pharmacy Speedy-Q System
The Speedy-Q system was implemented at Edenvale Hospital Outpatients Pharmacy to reduce patient waiting times. The pharmacy team conducted a study on waiting times- a common issue causing complaints and poor pharmacy experiences. Using the fishbone diagram, the root cause analysis revealed lengthy prescriptions, high patient volumes, staff shortages, inadequate infrastructure, and poor queuing systems as the main factors contributing to the issue. This was concerning to staff as working in a stressful environment impacts their mental and physical wellbeing. Pharmacy is the hospital's endpoint, causing outpatients to be exhausted from previous departmental consults and unable to queue for extended periods. Before Speedy-Q, waiting times ranged from 1 hour 15 minutes to 3 hours. Patients waited longer at pharmacy compared to the overall patient journey. Staff morale was affected, with staff taking sick leave four times a month. Due to human resource constraints and limited financial resources, a lean management approach was adopted, focusing on using available resources as a solution to the challenge. The dispensing process was restructured by implementing an innovative system to attain radical change and combat the long waiting times. Over its 21-month period, Speedy-Q has displayed a 78% reduction in waiting times.
Date: 2025/11/11
Version: 0.1
Tags:
Patient Waiting Times
Pharmacy Innovations
Public Health Innovations
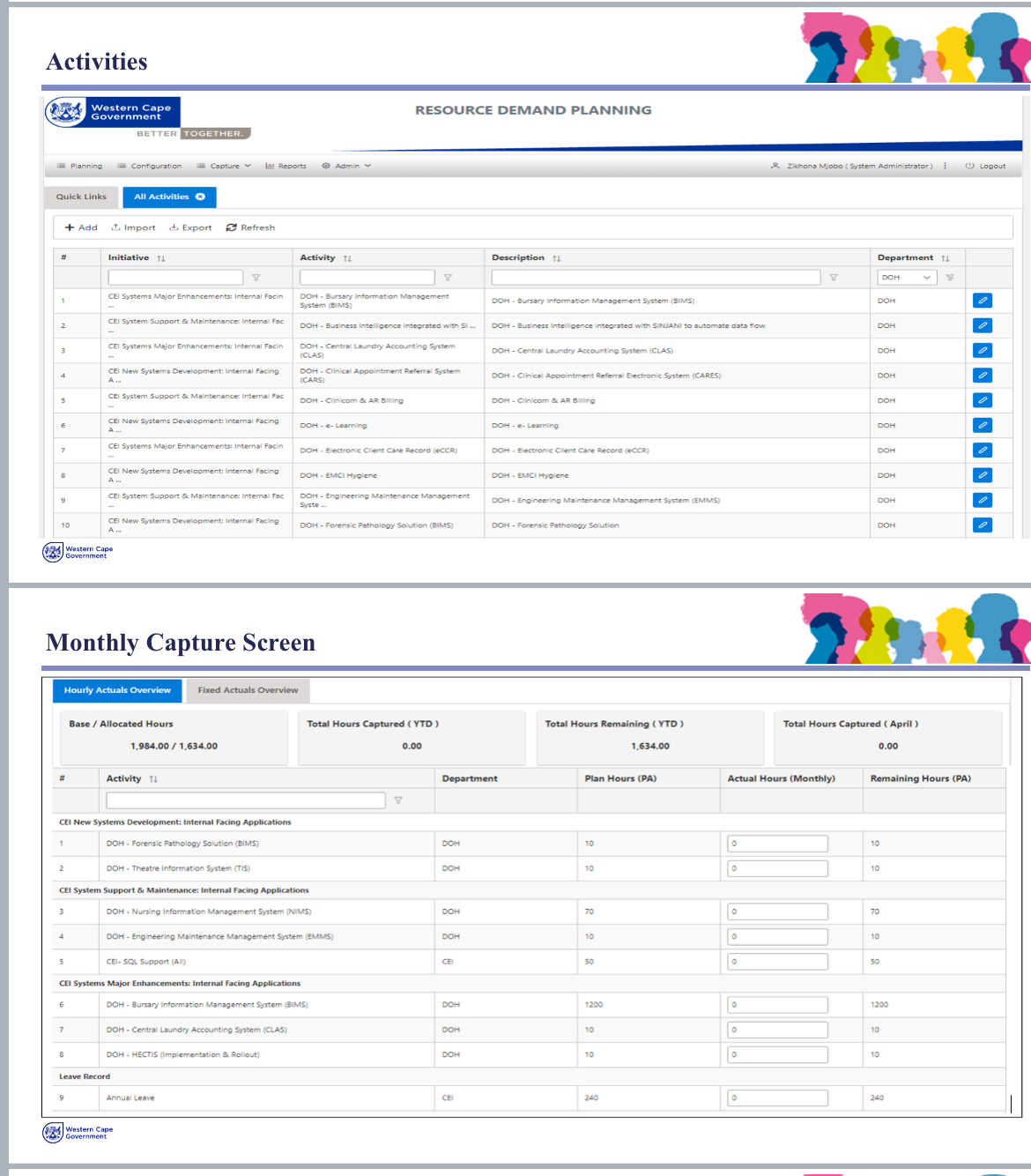
Demand Management Dashboard
The Department of Infrastructure (DOI) initiated the Demand Management Dashboard project to streamline, organize, and manage procurement activities across various programs. This web-based interactive tool serves as a comprehensive resource for all demand management-related requirements, including strategic sourcing, procurement planning, compliance, and procurement reporting. The solution offers robust data analytics, reporting, amendments, and guidance, significantly enhancing service delivery. The Demand Management Dashboard automates data capture, reporting, and compliance checks, ensuring a systematic, efficient, and transparent procurement process. Over the past 12 months, notable enhancements, such as integrating a chatbot using MS Copilot to assist staff with demand management queries, have further improved efficiency and transparency. By leveraging existing Microsoft tools like Excel Online, Power Apps, Power BI, MS Forms, and Power Automate (including AI models), the DOI eliminated the need for additional expenditure while achieving real-time visibility into procurement activities.
Date: 2025/11/11
Version: 0.1
Tags:
Microsoft Forms
Procurement Efficiency
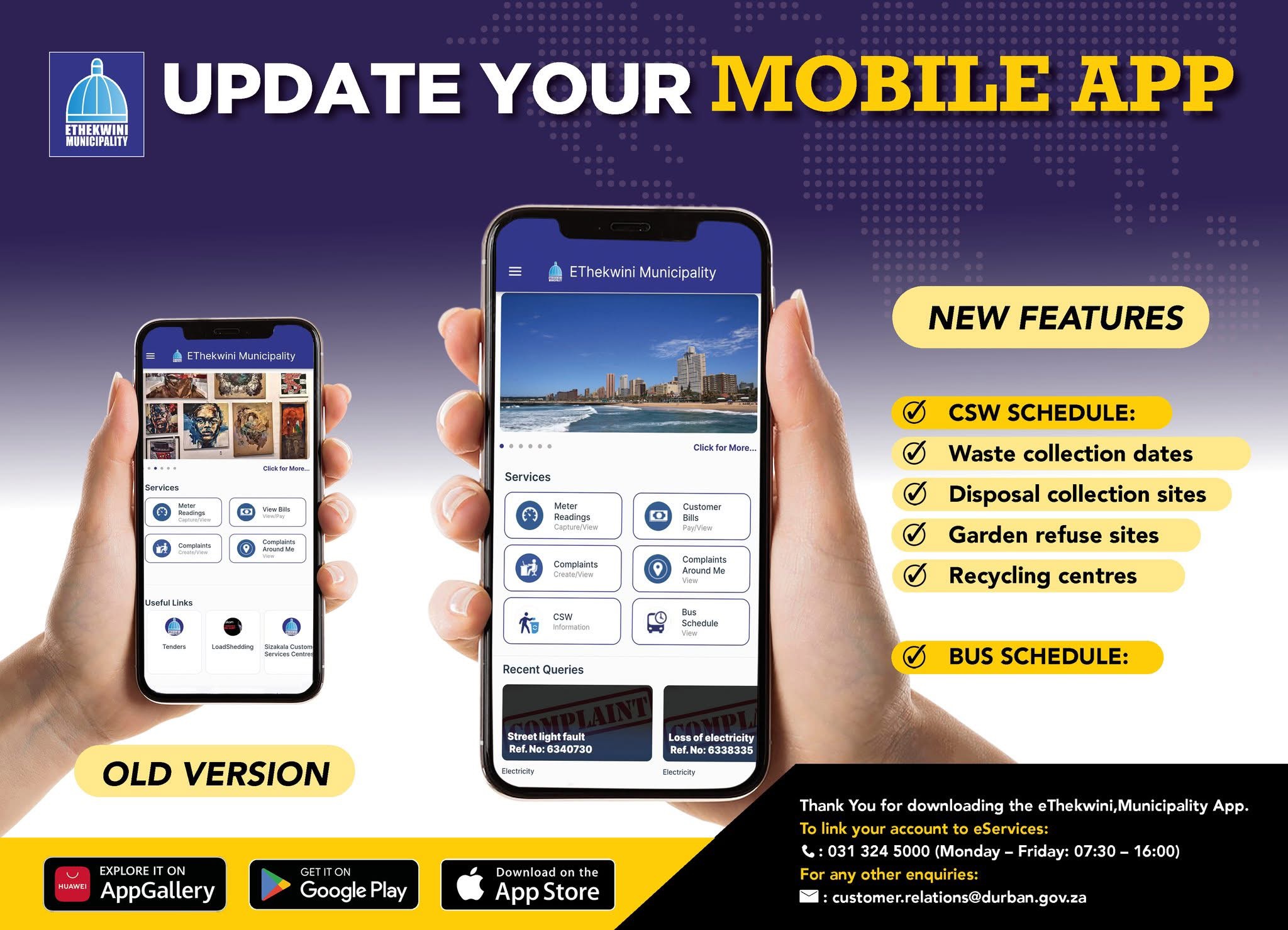
Ethekwini Mobile App
Customer Services within eThekwini Municipality is continuously exploring convenient and user-friendly platforms for customer engagement, one of which is the redesign of the mobile application, in order to offer a technology driven platform for the eThekwini citizen that requires minimal human interaction, improves customer engagement and promotes customer excellence. eThekwini Municipality currently has a customer focused mobile application which was commissioned in 2014, launched to the public in 2019 and Re- launch on the 23 July 2023. The mobile application offers the customer very basic and limited functionalities in relation to the vast services offered by the municipality. The eThekwini Mobile App is aimed at improving the engagement of customers with the Municipality by offering a quicker platform. This leads to the reduction of contact centre calls as well as foot traffic within the walk-in centres. The app also enables citizens to engage with the municipality in an efficient manner with shorter response times.
Date: 2025/08/22
Version: 0.1
Tags:
Local Government Innovation
Municipal App
Government In-house Solution

WCED ePortal
The Western Cape Education Department ePortal is an education-centric, large-scale distribution platform that provides teachers, learners and parents with online tools and resources to offer learners opportunities to improve educational results and throughput and to guide them to integrate into a technology-driven society and jobs market. The ongoing vision is to be the preferred delivery and engagement platform for digital educational content that addresses most educational needs, hosted within a curriculum focused ecosystem. WCED curriculum planners responded to school closure and disruption by developing more than 24 000 resources in three official provincial languages, at no cost to the end-user, and in alignment with the South African curriculum (CAPS). 31 000+ resources are hosted on the ePortal, readily available to everybody with internet connectivity.
Date: 2025/08/22
Version: 0.1
Tags:
eLearning
Government In-house Solution

Court Watching
The Court Watching Brief is an initiative of the Department of Police Oversight and Community Safety to enhance its ability to perform oversight over the South African Police Service as mandated by Section 206 (3) of the Constitution. One of the challenges that was identified by the Court Watching Brief in the Western Cape province, was an increasing number of court cases that were either withdrawn or struck off the roll. To deal with this challenge, the Court Watching Brief (CWB) business plan was drafted and approved in April 2023 which operationalizes its’ service delivery plan for the 2023/24 financial year. The CWB covers all courts located within the six magisterial Districts of the Western Cape Region. The CWB identifies criminal cases to be monitored in support of the provincial vision and strategic objectives. These priority cases may include gender-based violence (GBV), murder, gang-related and related murder cases and criminal cases from the crime hot-spot areas. The primary objective of the CWB programme is to promote professional policing, police accountability and contribute towards increasing service delivery by the police. The oversight is performed by visiting all 56 Magisterial Courts in the Western Cape to monitor police conduct as well as the efficiency and effectiveness of the South African Police Service (SAPS). The primary objective of the Court Watching Brief is to contribute towards promoting professional policing and accountability in line with the National Development Plan. In order to make this work more efficient, they developed a solution that automated their processes and improved their offering.
Date: 2025/08/20
Version: 0.1
Tags:
Government I-nhouse Solution
Court Watching Brief
Community Safety and Security
Police Efficiency
MS Forms

Linkage to Care
Community Based Services (CBS) are a critical tool in assuring the health of communities in resource poor settings. They have the tools to provide a comprehensive set of services which include nutrition, wound care, home based rehabilitation, adherence to therapy, palliative care and psychosocial support. They have been shown to reduce re-admission rates to hospital. There are 850 Community Health Workers and 62 registered nurses who provide CBS to the 1.1 million residents in the Klipfontein Mitchells Plain Substructure. The challenge is that these services are under-utilised due to administrative failures and inefficiencies in referring these patients. Less than 500 CBS referrals were completed in 2021. An informal audit revealed that contributory factors to low referrals included lack of staff awareness of available services, how to access these services, limited access to paper-based referral forms, limited administrative support to ensure paper forms were scanned/e-mailed and frequent scanner/computer failure. This meant that the limited referrals that were actually completed, often never reached the destination, to the detriment of the patient. It is for this reason that a Doctor at Mitchells Plain Hospital came up with a solution.
Date: 2025/08/19
Version: 0.1
Tags:
Public Health Solutions
Government In-house Solutions

Central Chronic Medication Dispensary and Distribution (CCMDD)
South Africa has experienced an unpredicted growth in patients requiring access to long term therapies driven in part by universal access to Antiretroviral Therapy (ART) and steady increases in patients with non-communicable diseases (NCD) requiring chronic therapy. There is an over extension of public sector health care facilities creating strain on available resources and has contributed towards medicine shortages and challenges in the quality of care provided. The experience of patients is one of protracted waiting times and often congested facilities. The CCMDD programme identified an opportunity to target the long term therapy category and provide an alternative, more convenient solution for stable patients to access chronic medicine. Prescriptions would be dispensed and packaged offsite, and delivered to pre-assessed external pick-up points (PuPs) to provide the patient with a location that may be nearer to their homes or work place and result in reduced transport costs and decrease the economic burden on the patient. Prescribing would be done by public health facilities and dispensing and PuP services would be offered through private contracted parties. An ICT system was developed to manage the data transfers through the value chain from prescription to patient collection.
Date: 2025/08/13
Version: 0.1
Tags:
Digital Health System
Pharmacy Innovation
Public Health Solutions
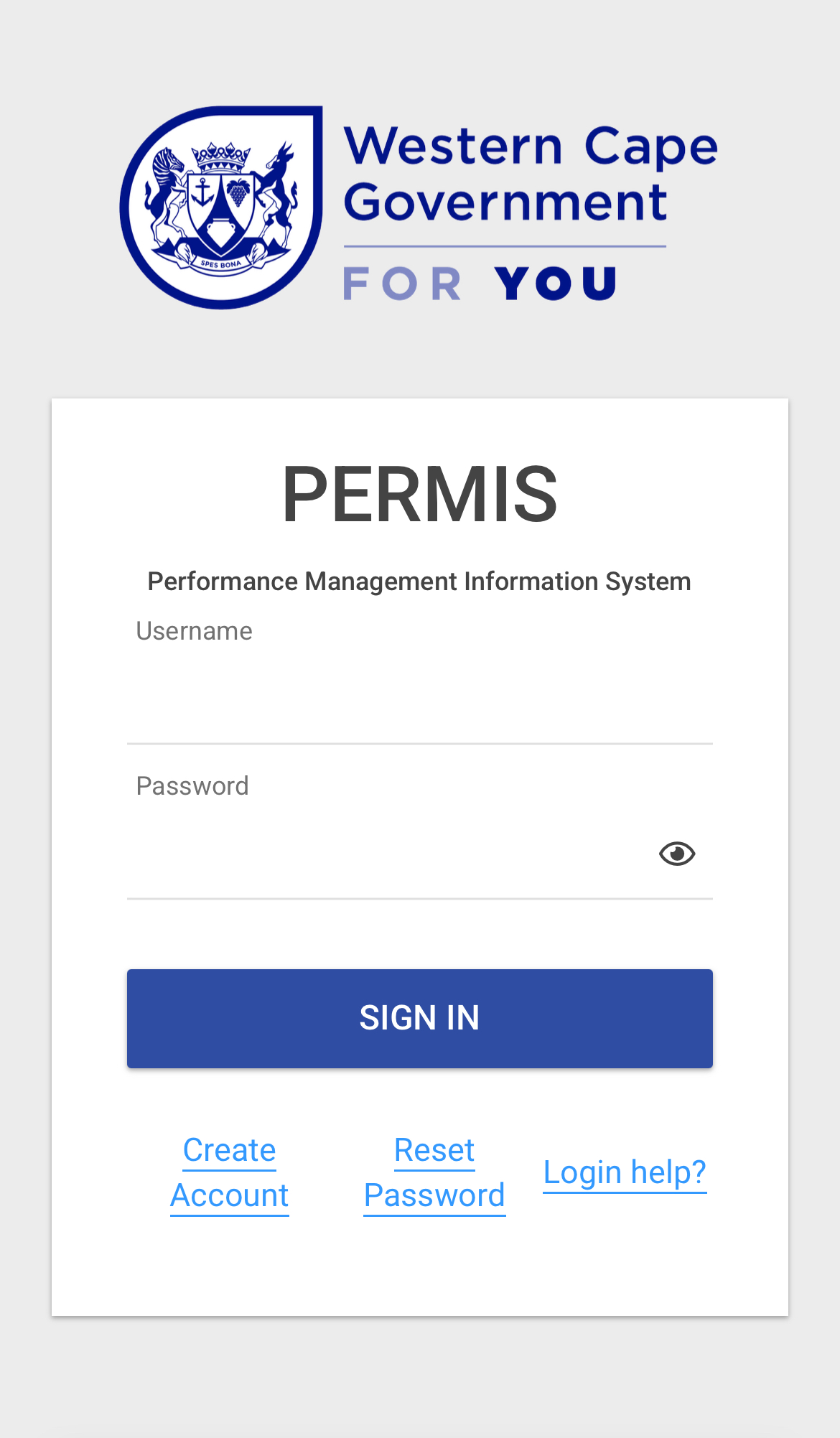
Performance Management Information System (PERMIS)
Historically performance contracting and evaluation was done manually, using MS Excel and Word, which proved to be time consuming and inefficient. This process also lacked transparency and governance from an ICT and people management perspective. As businesses matured, they looked at innovative ways to optimise some of the HR processes such as the performance management processes. The goal was to improve the process by moving away from the paper-based way of working, towards an PERMIS was developed to bring about standardisation of performance management processes in WCG as well as addressing process transparency and governance in managing employee performance. The Ce-I and People Management Branches note that the ever-increasing complexity of performance management necessitates continual improvement and reiteration of PERMIS so that employee performance in the province is objectively measured, and optimised. automated process and workflow.
Date: 2025/08/07
Version: 0.1
Tags:
Human Resource Solutions
Government In-house Solution
Performance Management
.jpeg)
Digital Patient Journey (HMS2)
The project is transitioning the Eastern Cape Department of Health from a predominantly manual patient medical record system that integrates other systems within the digital health landscape in South Africa, that includes NHLS, SANBS, HPRS etc. The system that is deployed is called HMS2, which is a inhouse developed system that maintains a shared medical record, allowing for the electronic recording and sharing of patient journeys (encounters and episodes) within and between healthcare facilities. This significant advancement allows the EC DoH to access real-time patient information across implemented healthcare facilities.
Date: 2025/08/06
Version: 0.1
Tags:
Public Health Innovations
Government In-house Solution
Health Management System
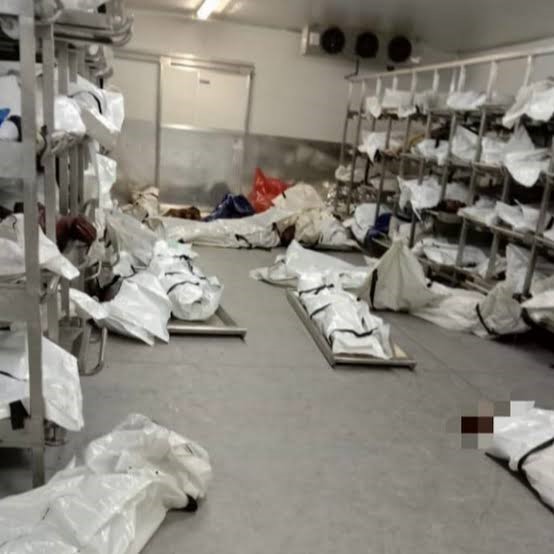

Digital Fingerprint for Pathology Services
The idea of the solution came after a Pathology Services official was part of the repatriation team that went to Nigeria to collect the mortal remains of those that died after the collapse of a church building in 2014. The challenge observed here was that families had to wait a long time to get closure on the identity of their loved ones. This is the same challenge that faces forensic pathology services where families wait a long time for DNA or fingerprint verification on bodies that cannot be identified using facial recognition. In addition to this, there was also a challenge of unidentified bodies that were piling up in mortuaries. The solution to deal with this challenge was a biometric solution that was the outcome of collaboration between CSIR and Bronkhorstspruit Pathology Services
Date: 2025/08/06
Version: 0.1
Tags:
Pathology Services
Biometrics
Unidentified Deceased Bodies

E-Recruitment System, Eastern Cape Province
The main reason for developing the e-recruitment system was to improve the turnaround time of the whole recruitment process which was a long period due to the process of typing a Masterlist, using an Excel spreadsheet. Masterlist was delaying the recruitment process since some jobs had more than 2000 applicants. This required more resources in terms of personnel and time. As each applicant applies for a job, the Z83 and masterlist is generated by the system, Recruitment officials can view applicant profiles and download the applicants’ files for the job before and after the closing date.
Date: 2025/08/04
Version: 0.1
Tags:
Human Resource Solutions
Government In-house Solution

E-Recruitment System, Limpopo Province
The E-Recruitment Platform started to address inefficiencies in the recruitment processes which were manual and time consuming. The traditional method of managing job vacancies and applications were manual, which resulted in delays and created an administrative burden. Based on the STATS SA e-Recruitment model, the system introduced key innovations that streamline recruitment processes. The system allows for efficient publication of vacancies, automated receipt and screening of applications, and comprehensive reporting features.
Date: 2025/08/01
Version: 0.1
Tags:
Human Resource Solutions
Government In-house Solution

The BizPortal Platform
The BizPortal is a platform that was developed by the Companies and Intellectual Property Commission (CIPC) to offer company registration and related services in a simple, paperless, and seamless digital way. It was developed in response to the quest for improving the ease of doing business in South Africa, especially starting a business. The challenges that have been addressed through the BizPortal include a reduction in turnaround times in company registrations. According to the World Bank Report 2019, it took over 40 days to start a business in South Africa. Starting a business not only involves registering with the CIPC, but it also includes tax registration, Unemployment Insurance Fund (UIF) and Compensation Fund registration. With the introduction of the BizPortal, all these services can now be done in a single online application process that can be concluded within a few minutes or up to 24 hours.
Date: 2025/07/17
Version: 0.1
Tags:
Economic Development
Government In-house Solution
Intergrated Service Access
E-Recruitment System, Gauteng Province
The Gauteng E-Recruitment System covers the whole recruitment process in one platform i.e. from placement of adverts, automated creation of unique reference numbers for each advert, application with SMS notification and shortlisting criteria, electronic shortlisting capability, and Management reports on advertising expenditure, adverts placed, applications received and shortlisted per department as well as per reference.
Date: 2025/07/17
Version: 0.1
Tags:
Government In-house Solution
Human Resource Solutions